Duke Medicine Timeline
- Child-proof safety caps
- North Carolina Cerebral Palsy Hospital opens
North Carolina Cerebral Palsy Hospital opens, established with federal funds on property donated by Duke University. It is later renamed Lenox Baker Hospital.
- Cerebral palsy hospital dedicated
North Carolina Cerebral Palsy Hospital is dedicated with 40 beds. It is later renamed to Lenox Baker Hospital.
- Nurses' housing
Hanes House for Nurses opens.
- BSN degree program
In response to the challenges of greater patient responsibility for nurses, the School of Nursing launches a four-year professional program leading to a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) degree.
- Duke Poison Control Center Opens
The Duke Poison Control Center is organized, becoming the second such center in the United States.
- Duke Center for Aging
- First open-heart surgery
Duke University Medical Center’s first open-heart surgery performed by a team led by Drs. Will C. Sealy, Ivan W. Brown, and W. Glenn Young.
- Cancer research
R. Wayne Rundles leads the creation of the Southeastern Cancer Chemotherapy Cooperative Study Group and chairs the group for ten years.
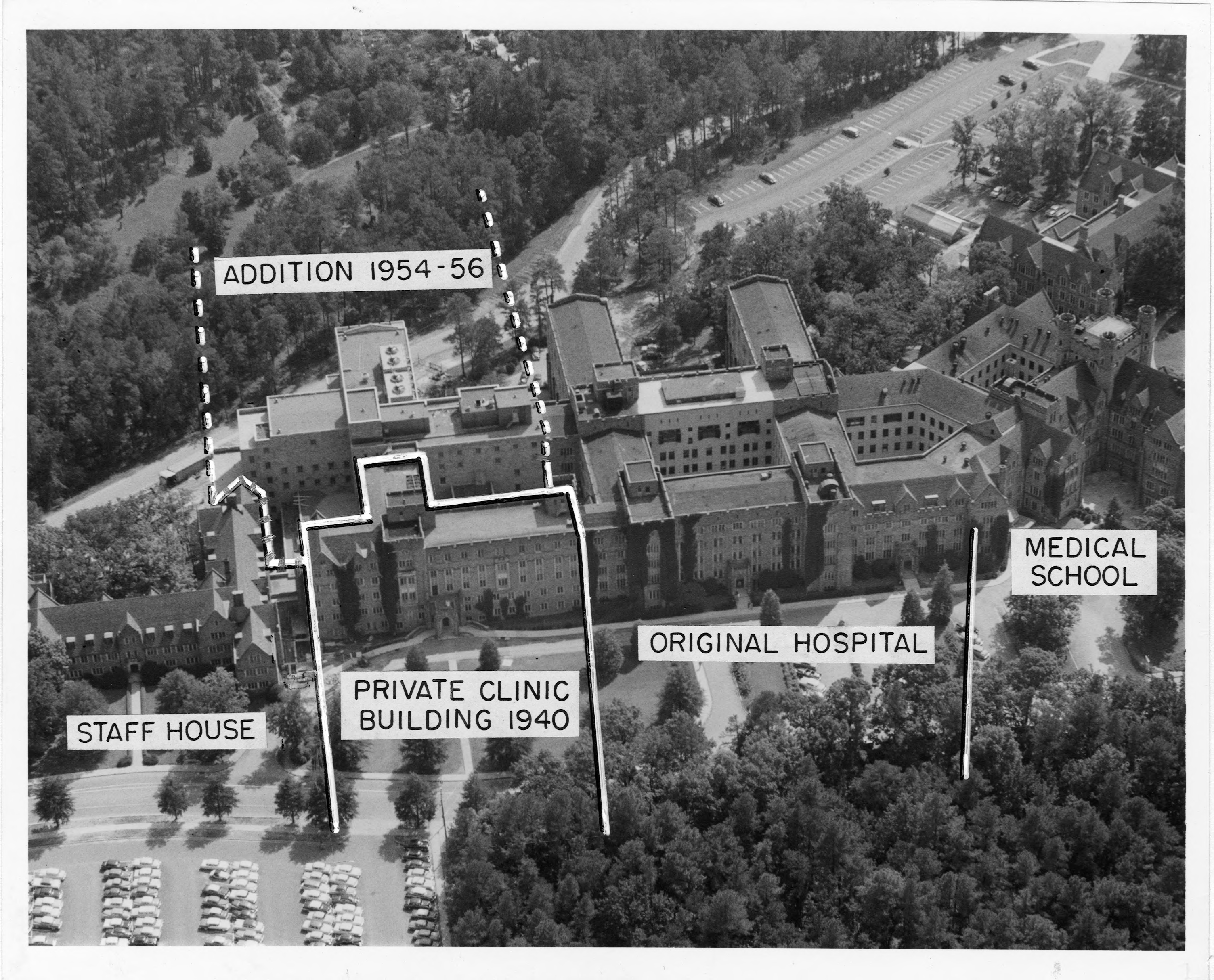
- Medical Center expansion
- Units renamed
The School of Medicine and Hospital are renamed "Duke University Medical Center."
- Graduate nursing program
Under the leadership of Thelma Ingles, professor and chair of the Development of Medical-Surgical Nursing, Duke develops the Clinical Nursing Specialist program, the first master's of its kind in the United States.
- Physician-Scientist training program
Duke’s signature Physician-Scientist training program is inagurated under the leadership of Drs. Handler, Stead, and Wyngaarden. A forerunner of NIH’s Medical Scientist Training Program, it puts Duke medical students into research experiences for 9 months of their training.